Condyloma Anal ( Genital Warts )
Genital warts, also known as condylomata acuminata or venereal warts, are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted diseases. New genital wart infections affect about 5.5 million Americans each year.
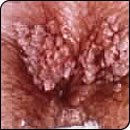
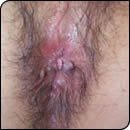
As the name suggests, genital warts affect the moist tissues of the genital area. They may look like small, flesh-colored bumps or have a cauliflower-like appearance. Sometimes they may be only 1 to 2 millimeters in diameter. In other situations, the warts may multiply into clusters, which can be quite large.
In women, genital warts can grow on the vulva, the walls of the vagina, the area between the external genitals and the anus (perineum), and the neck of the uterus (cervix). In men, they may be found on the tip or shaft of the penis, the scrotum or the anus. They can also develop in the mouth or throat of a person who has had oral sexual contact with an infected person.
Although genital warts can be treated, they are a serious health concern. The virus that causes them – the human papillomavirus (HPV) – has been associated with cervical cancer. It has also been linked with other types of genital cancers.
The signs and symptoms of genital warts
- Tiny, pink or red swellings in your genital area that grow quickly
- Several warts close together that take on a cauliflower shape
- Itching or burning in your genital area
Causes
Like warts that appear on other areas of your skin, genital warts are caused by a virus that infects the top layers of your skin. There are more than 100 different types of HPV. Yet only a few types of HPV infections can cause genital warts. They are highly contagious and spread through unprotected sexual contact with an infected person. About two-thirds of people who have sexual contact with someone who has genital warts develop the condition – usually within one to six months of contact.
Risk factors
Having unprotected sex with multiple partners increases your risk of becoming infected with HPV. Other risk factors include having another sexually transmitted disease, poor nutrition and hygiene, and medical conditions that suppress the immune system. Sometimes warts may also occur during pregnancy, possibly due to changes in the immune system.
When to seek medical advice
See a doctor if you have developed bumps or warts in your genital area. Also, talk to your doctor if you have a sexual partner who has developed genital warts or has had a diagnosis of them.
For women, it's important to have a pelvic exam and Pap test, which can help detect vaginal and cervical changes caused by genital warts or the early signs of cervical cancer, a possible complication of HPV infection. If you're sexually active, talk to your doctor about how often you need to have a Pap test. If you've had genital warts, you may need to have a Pap test every three to six months, depending on the severity of your condition. After having three normal Pap tests in a row, you can usually follow a yearly routine.
Complications
HPV infection has been linked with cervical cancer. Certain types of HPV also are associated with cancer of the vulva, cancer of the anus and cancer of the penis. Most types of HPV don't lead to cancer, but it's still important for women, particularly for those who have been infected, to have regular Pap tests
Genital warts may cause problems during pregnancy. They can enlarge during this time, which may make it more difficult to urinate. Warts on the vaginal wall may affect its ability to stretch during the birth. In rare cases, an infant born to an infected woman may develop warts in the throat, which may require surgery to prevent airway obstruction.
What is HPV? I understand that HPV is the main cause of cervical cancer. How does it cause cancer?
HPV is the acronym for the human Papiloma virus, which causes a sexually transmitted infection. Various strains of HPV are responsible for at least 95 percent of cervical cancer.
When exposed to HPV, the immune system in most women prevents the virus from causing harm. But in a small number of women, the virus can live for years and eventually convert cells on the cervix into cancer cells. These cellular changes happen very slowly. At first, the cells only show signs of a viral infection. Later they become precancerous (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia) and can eventually progress to invasive cervical cancer.
It's not clear why the immune systems in some women make them more susceptible to cervical cancer. Tobacco use increases the risk of both precancerous changes and cancer of the cervix. The exact mechanism that links cigarette smoking to cervical cancer isn't known.
The best ways to avoid infection with HPV are to:
- Avoid having multiple sexual partners.
- Use condoms.
- A promising new vaccine to prevent HPV infection is being studied. But the vaccine is experimental and won't be available to the public for at least several years.
Treatment
Doctors can help you get rid of an outbreak of warts with medications or surgical treatments. Sometimes medical treatment can take care of the virus that causes genital warts as well. If the underlying virus isn't completely eliminated, however, genital warts may reappear even after treatment.
Medications
Topical treatments are available that can be applied directly to your skin. These include:
- If warts are very small and are located only on the skin around the anus, they can be treated with medications, which are applied directly to the surface of the warts. This method, while relatively simple in concept, must be carried out with great care and precision by a physician to prevent injury to the normal skin surrounding the warts. This method usually requires several applications performed at various intervals over several weeks.
- Imiquimod (Aldara)
- Ksharkarma
- Agnikarma
- Podofilox (Condylox)
- Trichloroacetic acid
- Surgery : Surgery may be necessary to remove larger warts or warts that don't respond to medications. Surgical options include:
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen (Cryosurgery)
- Burning with electricity (Radio Frequency Cauterization) : Another form of treatment involves more rapid destruction of the warts using electrical cautery, surgical removal or a combination of the
- Laser Treatments : Laser surgery may also be used These procedures provide immediate results but must be performed using either a local anesthetic – such as Novocain – or a general or spinal anesthetic, depending on the number and exact location of warts being treated.
- Don't try to treat genital warts with over-the-counter medications, which aren't intended for use in the moist tissues of the genital area. Doing so can cause even more pain and irritation.
Must I be hospitalized for treatment?
No. Almost always, the cautery and excision technique can be performed on an outpatient basis, and the patient can go home after the procedure.
Must I be hospitalized for treatment?
No. Almost always, the cautery and excision technique can be performed on an outpatient basis, and the patient can go home after the procedure.
How much time will I lose from work after a cautery treatment?
This depends on each individual situation and the extensiveness of warts removed. Most people are moderately uncomfortable for a few days after treatment, and pain medication may be prescribed. Depending on the extent of the disease, some people return to work the next day, while others may remain out of work for several days.
Will a single treatment cure the problem?
Not in most cases, unfortunately. Even with the cautery and surgical treatments that immediately destroy existing warts, many patients develop new warts after treatment. This occurs because viruses that cause the warts can live concealed in tissues that appear normal for up to six months or longer before another wart develops. New warts will often develop from the virus that was already present in the tissue, but these are not recurrences of warts already treated.
As new warts develop, they usually can be treated in the physician's office, using either a chemical solution or the electrical cautery procedure. These treatments are performed every few weeks initially, then less frequently as new warts become smaller and less numerous.
Sometimes new warts develop so rapidly that office treatment would be quite uncomfortable. In these situations, a second and occasionally third outpatient surgical visit may be recommended.
How long is the treatment usually continued?
Follow-up visits are necessary for some months after the last wart is observed to be certain that no more warts occur from viruses living in the cells of skin.
What can be done to avoid getting these warts again? Prevention
In some cases, warts may recur repeatedly after successful removal, since the virus that causes the warts often persists in a dormant state in body tissues. Following are tips to avoid recurrence and re infection:
- Continue observation for several months after the last wart has been spotted to improve the chances that both the warts and the underlying virus that causes them have been eliminated
- Abstain from sexual contact with individuals who have anal (or genital) warts. Since many individuals may be unaware that they suffer from this condition, sexual abstinence or limiting sexual contact to marriage relationships will reduce your potential exposure to the contagious virus that causes these warts. As a precaution, sexual partners ought to be checked, even if they have no symptoms.
- Practicing safe sex can reduce the risk of genital warts. Yet using condoms doesn't eliminate the risk entirely because they still may allow you or your partner to come in contact with infected skin. If warts are visible on you or your partner's genital area, avoid sexual contact until the warts are treated. If you've developed genital warts for the first time, inform your sexual partner so that he or she can get treatment and take precautions to prevent spreading the condition to others