Hemmorrhoids ( Piles )
Hemorrhoids or Piles as is generally known is a very common disease. About 70% of the population have at some time in their lives suffered from piles or have had experienced some symptoms related to it.
We will first try to understand what Piles / Hemorrhoids are. Piles or Hemorrhoids are actually, distended veins in the anal canal. Veins tend to stretch under pressure. When veins in the lower part of the rectum or anus stretch, swell or descend in to the anal canal, i.e. when they prolapse or protrude in to the canal they are considered as Piles/Hemorrhoids.
The set of veins inside the rectum when distended result in internal hemorrhoids and the set of veins under the skin around the anus when distended result in External Piles.
Some other factors also contribute to the prolepses of the veins. They are long standing constipation, leading to straining while passing stool, pregnancy, weakening of the muscles supporting the veins due to ageing etc. One may also have a hereditary tendency to develop piles

If you have any of the following symptoms you are probably suffering from Hemorrhoids- Piles.
1. Bleeding from the anus :
- after defecation (passing stool)
- during defecation
- during and after defecation
usually without pain but in some conditions with pain.
2. Constipation
3. Itching
4. Protrusion of a mass from the anal canal (can be felt digitally).


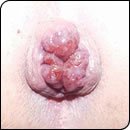
Causes
- Pregnancy
- Straining during child birth
- Obesity
- Lifting heavy weights over a long period
- Sitting or standing for a long time
- Chronic constipation accompanied with straining to evacuate the bowels
- Repeated diarrhea and dysentery
- A habit of suppressing the urge to defecate
- There may also be an inherited tendency to develop Hemorrhoids / Piles.
Types of Hemorrhoids / Piles
Hemorrhoids / Piles can be classified in two ways
I. As per their site of development
- Internal hemorrhoids / piles
- External hemorrhoids / piles
II. As per the stages of the diseases
- First degree hemorrhoids
- Second degree hemorrhoids
- Third degree hemorrhoids
- Fourth degree hemorrhoids
First degree Hemorrhoids: Is the condition when the mass (The structure with the veins) projects slightly into the anal canal, but only when the veins are congested i.e. during defecation / passing stool.
In this stage the patient will have no mass protruding from the anus.
Second degree Hemorrhoids: The mass protrudes out of the anus, but only during defecation. The hemorrhoidal mass returns into the anal canal spontaneously after passing stool as soon as the accompanied straining stops.
Third degree hemorrhoids: The hemorrhoidal mass protrudes from the anus during defecation or on exerting force and remains protruded until forced back into the anus digitally ( with fingers) .
Fourth degree hemorrhoids: The hemorrhoidal mass (Piles) remains protruded (out of the anus) at all times and can not be forced into the anal canal with the help of the fingers.
Treatments
1. Oral medicines, like laxatives, stool softeners etc and local anti inflammatory creams and warm water sits bath can help to reduce the symptoms. However second, third and fourth degree piles can not be cured with just oral treatment.
2. Barran band ligation: One or two special kind of rubber bands are tied around the base (slipped to the base with the help of a special instrument,) of the internal hemorrhoids. The pressure exerted by the rubber band stops the circulation in the tied off pile mass. Gradually, within seven to ten days, the pile mass falls off. This is comparatively a simple procedure and is usually painless. It is performed under anesthesia or even without anesthesia. This treatment is indicated in most cases of second and third degree hemorrhoids.
3. Sclero therapy: A chemical solution is injected around the veins of the hemorrhoids. This treatment is indicated in first to second degree piles. Sclero therapy is not preferred by most surgeons now. (See detail)
4. Crayo surgery: The affected part is freezed by nitrous oxide or carbandioxide gas. This cuts off the circulation and destroys the pile mass. This is indicated in first to third degree hemorrhoids. This method is now not preferred by most surgeons. (See detail)
5. Cauterization: The pile mass is shrunk with the help of bursts of electric current. Indicated in second to third degree piles. This method is not now practice by most surgeons. (See detail)
6. Infrared photo coagulation: Infra red rays are given to an internal hemorrhoid which cuts off the circulation in it. Some heat may be experienced during the procedure. The pile mass falls off within a few days. There may be some bleeding. Indicated in second to third degree piles. (See detail)
7. Laser therapy: The hemorrhoid mass is vaporized by a laser beam. Using laser beams for surgery is beneficial since it minimizes pain and bleeding. Indicated in second to fourth degree piles. (See detail)
8. Conventional surgery: (Open and closed hemorrhoidectomy) An operation is performed under suitable anesthesia, the vein in the pile mass is tied / legated and the mass is cut off with a surgical knife or scissors. The wound caused is closed or kept open. The surgery requires 24 to 48 hours hospitalization. Indicated in 3rd to 4th degree piles. (See detail)
9. Kshar Patan (Ksharkarma): Ksharpatan is a non surgical procedure of Ayurveda used to effectively treat hemorrhoids. A medicine (chemical) derived from a combination of various herbs is applied to the pile mass with the help of a special slit proctoscope. It is a type of chemical cauterization. This method is highly effective, cost effective and can be performed on OPD level.
The patient may require more that one sitting. The Ksharpatan method of treating piles has been described in detail in the ancient Shusrut Samhita. The details of preparation of the herbal combination used can also be got from the Shusrut Samhita. This method of treating piles- hemorrhoids was forgotten for years, but thanks to the research in the field of Ayurveda Surgery, it has made a comeback.
This simple procedure is so effective and safe that it is now slowly becoming popular in India like the Kshar-sutra legation method of treating Ano-rectal fistulae.
This method is indicated in 2ndo 3rd degree Piles- Hemorrhoids (See detail)
| Classification | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
1st Degree : Hemorrhoidal mass projects slightly into the lumen of the canal when the veins are congested at defaecation.
|
|
2nd Degree : Hemorrhoidal mass appears externally while the patient is straining but returns spontaneously into the anal canal when the motion has been passing and the defecating effort has ceased.
|
|
3rd Degree : Hemorrhoidal mass protrude during defaecation and also on exertion of any kind of force and remain protruded until digitally replaced within the anus
|
|
4th Degree : Large Hemorrhoidal mass remains protruded almost permanently and cannot be properly returned into the anal canal digitally
|
|


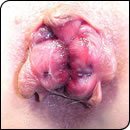



Prevention
To prevent hemorrhoids or Hemorrhoidal flare-ups:
Eat high-fiber foods.
Fiber (roughage) is the part of plant food that is not digested. It stays in your gut and is passed in the stools (faeces). Fiber adds bulk to the stools. This helps your bowels to work well, and helps to prevent some bowel and anal conditions.
Why is fibre important?
Stools (sometimes called faeces or motions) are usually soft and easy to pass if you eat enough fibre, and drink enough fluid. A diet with plenty of fibre will help to:
- Prevent constipation.
- Prevent diverticulosis (a common bowel condition).
- Prevent hemorrhoids (piles) and anal fissure (a painful condition of the anus).
- Reduce weight. Fiber is filling but not fattening as it has no calories and is not digested.
- Possibly reduce the risk of developing bowel cancer.
30 grams of fiber per day is recommended. However, the average person in the UK eats only about 20 grams of fiber each day.
High fiber foods include the following
- Whole meal or whole-wheat bread and biscuits.
- Whole meal flour used for baking and cooking.
- Fruit, vegetables, and nuts.
- Whole-grain breakfast cereals such as All Bran, Bran Flakes, Weetabix, Shredded Wheat, muesli, etc.
- Brown rice, and whole meal spaghetti and other whole meal pasta
A simple thing like changing your regular breakfast cereal can make a big difference.
Fiber supplements
You may need to take extra fibre supplements if you have constipation or other bowel problems. Several are available. You can buy them at pharmacies or health food shops. (https://www.almostthererescue.org)
- Unprocessed bran is the most common (and cheapest) fibre supplement. If you take bran, it is best to build up the amount gradually. Start with 2 teaspoons a day, and double the amount every 5 days until you reach about about 1-3 tablespoons per day. You can sprinkle bran on breakfast cereals, or mix it with fruit juices, milk, stews, soups, crumbles, pastries, scones, etc
- Some people find bran unpalatable, and you may want to try other fibre supplements such as ispaghula husk or methylcellulose. Ispaghula husk is also gluten-free.
- Have lots to drink when you eat a high fibre diet or fibre supplements. Drink at least 2 litres (about 8-10 cups) per day. You may find that if you eat more fibre, you may have some bloating and wind at first. This is often temporary. As your bowel becomes used to extra fibre, the bloating or wind tends to settle over a few weeks.
- Eat more fruits, vegetables and grains. Doing so softens the stool and increases its bulk, which will help lessen the straining that can cause hemorrhoids.
Drink plenty of liquids.
How much water and other fluids should you drink daily ? The National Research Council (NRC) uses a sliding scale of 1 milliliter (ml) of water for every calorie burned. This scale is not for women who are pregnant or breast-feeding, infants, children and older adults who are unhealthy. The NRC says the average man — who burns about 2,900 calories daily — needs 2,900 ml, or about 12 cups, of water each day. The average woman — who burns 2,200 calories daily — needs about 2,200 ml, or about 9 cups, of water each day. For your own calculations: One measuring cup (8 fluid ounces) of water equals 236 ml. But these cups don’t have to be filled with water. Solid food contains water. In an average diet, food provides about 3 to 4 cups of water each day. Men, because they generally are bigger and have more lean muscle tissue, on average need more water each day than women do.
Try fiber supplements
Over-the-counter products such as Metamucil and Citrucel can help keep stools soft and regular. Check with your doctor about using stool softeners. If you use fiber supplements, be sure to drink at least 8 to 10 glasses of water or other fluids every day. Otherwise, fiber supplements can cause constipation or make constipation worse. Add fiber to your diet slowly to avoid problems with gas
Exercise
- Stay active to reduce pressure on veins, which can occur with long periods of standing or sitting, and to help prevent constipation. Exercise can also help you lose excess weight.
- Avoid long periods of standing or sitting. If you must sit for long periods, don’t use an inflatable doughnut cushion to pad your chair. It can increase the pressure on the veins in the anus.
Don’t Strain
- Straining and holding your breath when trying to pass a stool creates greater pressure in the veins in the lower rectum.
- Go as soon as you feel the urge. If you wait to pass a bowel movement and the urge goes away, your stool could become dry and be harder to pass.
Self – Care
You can temporarily relieve the mild pain, swelling and inflammation of most Hemorrhoidal flare-ups with the following self-care measures :
- Apply an over-the-counter hemorrhoid cream or suppository containing hydrocortisone, or use pads containing witch hazel or a topical numbing agent.
- Keep the anal area clean. Bathe (preferably) or shower daily to cleanse the skin around your anus gently with warm water. Soap isn’t necessary and may aggravate the problem. Gently drying the area with a hair dryer after bathing can minimize moisture, which can cause irritation.
- Soak in a warm bath several times daily
- Apply ice packs or cold compresses on the anus for 10 minutes up to four times a day.
- If a hemorrhoid has prolapsed, gently push the hemorrhoid back into the anal canal.
- Use a sitz bath with warm water. A sitz bath fits over the toilet. You can get one at a medical supply store or some pharmacies.
- Use moist towelettes or wet toilet paper after a bowel movement instead of dry toilet paper
- These self-care measures may relieve the symptoms, but they won’t make the hemorrhoid disappear. See your doctor if you don’t get relief in a few days.

















